Example: Domain Knowledge
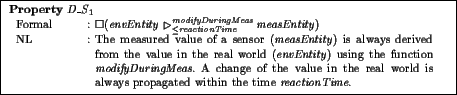
In this section of a description class the considered part of a system is described as it is. This means that the behavior of the system is described as it is without or despite of the machine. For example, the relationship between the measured temperature in a room and the temperature actually existing in the room belongs to the domain knowledge if the sensor is already installed in the room. Usually there are delays and deviations. The following example represents such a relationship.

Example: Domain Knowledge
Every statement that belongs to the domain knowledge has a unique name standing
after the keyword Property. In the example above this is
![]() .
Every statement is given formally, i.e. as a temporal logic
formula (after the keyword Formal) and in natural language (after the
keyword NL).
.
Every statement is given formally, i.e. as a temporal logic
formula (after the keyword Formal) and in natural language (after the
keyword NL).